Please refer to the animations below to gain an understanding of how the parts on your car function.
1. 4-stroke gasoline engine

A 4-stroke gasoline engine is an internal combustion engine that functions through four distinct stages: intake, compression, explosion, and exhaust. This engine utilizes a combination of air and fuel, which is ignited by the spark plug, generating force to propel the piston downward.
2. Inline engine

The inline engine, marked by the letter “I,” is the most basic and widely used engine design found in cars. In this design, the engine cylinders are arranged in a straight line.
3. Flat motor

The Flat engine, also known as a variant of the V engine, has an angle of 180 degrees between its cylinders. It offers the benefit of a low center of gravity, which is why Porsche has selected it as one of its primary engines.
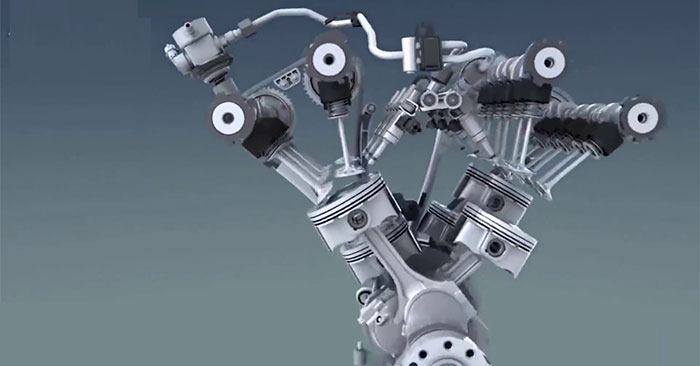
4. V engine

V-shaped engines have a more intricate structure compared to in-line engines. They offer the advantage of being powerful and quiet while remaining lightweight, making them a suitable choice for most car designs. Consequently, V engines are commonly utilized to equip larger car models.
5. Turbocharger

A turbocharger, also known as an engine turbocharger, is a device that utilizes exhaust gas from the engine to spin turbine blades. The spinning turbine blades then rotate a pump impeller, which forces fresh air into the combustion chamber. Compared to a naturally aspirated engine, a turbo engine has the ability to intake a larger amount of air.
VTEC is an intelligent variable valve control system that adjusts valve timing for optimal performance.

The VTEC variable valve control system was created with the aim of enhancing the performance and efficiency of internal combustion engines across various engine rpm ranges. By adjusting the opening angle of the valves, this system has the capacity to optimize the intake of fresh air into the engine.
A CVT is a transmission that can seamlessly change gear ratios without traditional fixed gears.

The CVT, or continuously variable transmission, utilizes a system of pulleys and belts to achieve seamless changes in transmission ratios, eliminating the need for distinct gears.
DCT is an abbreviation for dual-clutch transmission.

This transmission has two separate clutches that work independently, enabling faster and smoother gear changes automatically.
9. Differential

The differential is a gear system positioned on an axle that connects two wheels together. Its main function is to receive torque from the drive shaft and evenly distribute it to each wheel. By allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds, the differential helps maintain balance and stability for the vehicle, particularly during cornering.
This component can be found in every modern car and truck.


